Diagram
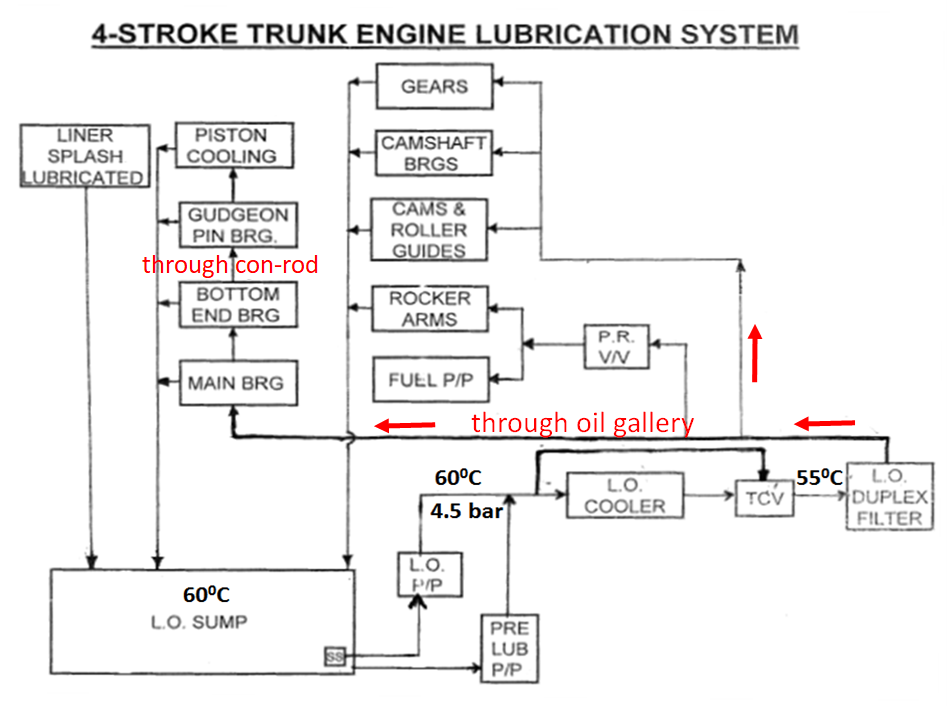
Working
The L.O. sump stores L.O. for lubrication and cooling of various engine components.
Engine driven (attached) L.O. pump takes suction from L.O. sump through a suction strainer which is located at inside the sump itself.
After L.O. pump oil passes through duplex type filters and through the L.O. cooler.
L.O. cooler may be Sea water or Fresh Water cooled. The pressure of L.O. is always higher than the cooling S.W./F.W. pressure to prevent S.W/F.W. leaking into the system in case of tube leakage .In case of leaking tubes L.O. will leak out.
The temperature of the L.O. after the cooler is controlled by a “Wax Type” thermostatic temperature control valve (it is a 3-way valve ). If temperature at the inlet to the cooler is higher than thermostatic valve setting, then the valve will be fully open to pass the full flow of L.O. through the cooler . If the temperature is below the set value, the thermostatic valve will bypass a part of L.O. and the rest passes through the cooler.
The oil is normally supplied to what is called as L.O. Gallery inside the entablature of the engine . Through the L.O. gallery L.O. is supplied to each of Main bearings, camshaft and attached p/p driving gears, the camshaft bearings, the camshafts and their roller guides, and through a pressure reducing valve to rocker arms, valve tappets and fuel pump plunger lubrication.
Once oil is supplied to the main bearings, it lubricates and cools the main bearing. Apart of the L.O. comes out of each bearing and falls back into the crank case and the rest of it passes through internal holes drilled through the crankshaft into each of the crankpins.
Oil comes out through a drilled hole in each of the crankpins and lubricates & cools the bottom end bearing of the connecting rod (con-rod) . Again part of the L.O. comes out of each bearing and falls back into the crank case and the rest of it passes through internal holes drilled through the con-rod into each of the piston pin (gudgeon pin).
Each gudgeon pin is thus lubricated and cooled by the supply of L.O. In some engine designs after lubricating gudgeon pin , a part of L.O. is used to for piston cooling. In other types a separate piston cooling spray nozzle with pressure reducing valve is fitted to the lower end of each liner which gets L.O. directly from L.O. gallery. This spray is used to cool the underside of the pistons. A part of L.O. falls back to the c/case while a part of it moves outwards and gets drained through the end of the piston boss and is finally taken down by the oil scraper ring.
Cylinder liner is splashed by the oil which falls down from various bearings & after piston cooling onto the moving con-rod , also the dipping of the con-rod , crank-webs into the L.O. in the c/case creates a splash . This L.O. “splash” mostly lubricates and cools the lower end of the liner . The oil control (scraper) ring spreads it during piston upward stroke onto the liner wall . During piston downward stroke oil is scraped down from the liner surface. {Note :In highly powered and long stroke trunk type engines , system oil ( or high TBN oil) may be directly supplied through quills directly to lubricate the liner}.
Function of L.O. is to provide lubrication and cooling at all places.
The valve operating mechanism consisting of push rod , rocker arm etc. is lubricated, by taking a supply of main L.O. through a pressure reducing valve . Pressure reducing will reduce the pressure to about 1.0 bar pressure .After lubrication and cooling of various components of v/v operating mechanism the oil falls back through the cam-case into the crank-case.
L.O. after pressure reducing valve , is also supplied in very small quantities(drop by drop only) to lubricate the plungers-barrels of bosch type fuel pumps of the engine (this doesn’t go back to the c/case as it will contaminate the L.O. with fuel oil)
L.O. is also supplied to cams , roller guides, camshaft bearings and also to the spray nozzles for lubricating the camshaft driving gears
The oil after falling into the c/case is drained to the L.O. sump provided just below the engine crank-case through strainer mesh provided normally on the forward and aft side of the engine crank-case. The L.O. sump is normally a part of the bedplate of the engine in 4-stroke, trunk type marine auxiliary engines (used as diesel generators) Crankcase will be provided by suitable breathers to prevent overpressure/vacuum inside the crank chamber.
Authored by:- C/E Shishir Dutt
Extra First Class Marine Engineer