The Previous Module
This module is a continuation of the previous module, where we understood the layout and working of a FWG plant. We purposefully made this a separate module to help you understand better and prevent the modules from being excessively long.
We will use the same diagram and point out all the components one at a time.
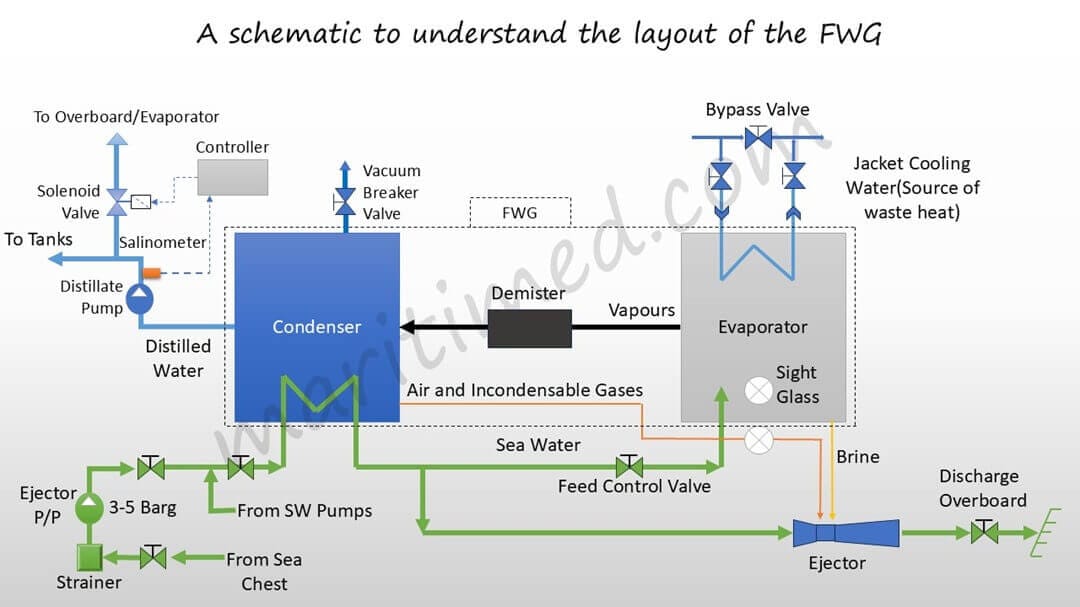
Sea Chest: The recess on the side of the ship’s hull which provides seawater to the suction of all the SW pumps, like CSW pump, Fire Pump, Ballast Pump, Ejector Pump, etc. Please note that we didn’t mention the emergency fire pump.
Strainer: It traps the foreign particles in the seawater, which would otherwise have entered the pump and could have caused damage.
Ejector Pump: Usually of Centrifugal type, this pump supplies SW to the FWG. The pressure is generally around 3-5 barg.
Feed Control Valve: This valve can either be a spring-loaded valve or a globe valve. It controls the feed rate of SW to the evaporator side of the FWG.
Brine Eductor-cum-Air Ejector: This equipment works on the venturi effect, based on the principles of Bernoulli’s Theorem. The SW acts as a motive fluid and is responsible for creating a vacuum at the neck.
Evaporator section of the FWG: This section uses the heat from the Jacket Cooling Water to heat up the seawater to form vapours under a vacuum condition.
Demister: This is generally made of wire mesh which makes the path of liquid in the vapour stream torturous, thus keeping the vapor stream free of seawater carryover.
Condenser section of the FWG: This section transfers the heat from the vapors to the seawater, as a result of which the vapors condense to form water.
Vacuum Breaking Valve: Closed during the normal operation of the FWG, this valve provides the air-tightness required to maintain the vacuum. This can either be a ball valve or a needle valve.
Distillate Pump: Just like the ejector pump, this is also a centrifugal pump that pumps the water formed in the condenser to the FW/Distillate tanks.
Salinometer: This sensor, fitted on the discharge of the distillate pump, measures the salinity of the FW and works on the conductivity principle. The higher the conductivity, the higher the salinity of the produced water.
Controller: Based on the signals received from the Salinometer, it sends the signal to operate the solenoid valve to prevent the saline water from reaching the tanks.
Solenoid Valve: This valve, normally closed, connects the distillate pump discharge to the feed line of SW or to the overboard line.
See you soon :)

The Next Module













